
Road Network Operations
& Intelligent Transport Systems
A guide for practitioners!

Road Network Operations
& Intelligent Transport Systems
A guide for practitioners!
Static detectors and probe vehicle measurement provide complementary views of the performance of the road network through roadside observation and by passively monitoring individual vehicles. These techniques are adequate, most of the time, for managing traffic operations. AID can improve their effectiveness in responding to accidents and planned events. Other sources of data that can help better manage a road network include:
During an incident, the mix of traffic data available to road operators is likely to change, with increasing amounts of information arriving from both reliable known sources (“trusted”) and unproven (“untrusted”) sources. Some of the information received may conflict with current knowledge - potentially highlighting a change in circumstances or new and unrelated incidents. The effective use and management of all data sources is critical to effective network operations, particularly during the incident management process.
A well-designed cost-effective traffic management operation needs to recognise the existence of other data sources and to provide the means to include them in its traffic and incident management strategy. Data sources and data owners, other than the highway authority or road operator include:
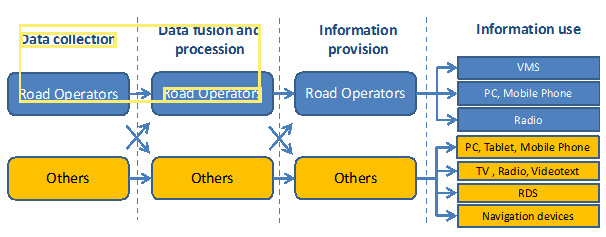
The figure below shows the role of other parties alongside road operators in the traffic data collection process. By way of illustration:
Whatever the source of the data, it needs to be assigned a level of trust by the road operator to help it prioritise sources and ensure that the reliance placed on a specific source is appropriate. Data sharing agreements between organisations should clearly specify each parties’ respective roles and responsibilities – and be formally documented (perhaps in a Memorandum of Understanding) and agreed by all parties. The road operator will also need to develop a policy and procedure for handling reports by the public – and to record this for its staff in an operations handbook.
The variety of other data sources available is matched by the variety of data formats and the trust that may be placed on the sources. The most cost-effective data sources for developed and developing countries are existing sources – but it is important to check that they are reliable and suitable if they were designed for another purpose (such as a weigh-in-motion sensor). A rigid definition of sources may not be relevant – and a traffic operator will need to apply discretion and judgment to the value of the reports received from them. Whatever the source, all data collected needs to include as a minimum - location information and a time stamp.
Where additional information is needed to improve traffic operations or incident management, site observers may be deployed to specific locations to collect survey data, report on traffic behaviour at planned events or to provide real-time information by voice (mobile phone or private mobile radio) or handheld computer at the location of an incident.
Standardisation of data formats, protocols and communications interfaces is desirable to avoid misunderstandings or conflicts between organisations – such as the data provider (a Police Incident Control Centre) and the data receiver (the Traffic Control Centre – TCC).
If a data interface is required, a technical interface standard can help ensure that a TCC can add new sources easily - whether the data is provided from another system (Centre to Centre, C2C) or directly from a device located in the field (Centre to Field, C2F). Examples include: